1.3 Task Configuration
This section introduces the definition of a federated task and how to run algorihms on different tasks in our frameworks. A federated task is defined as optimizing an objective on a given data distribution.
Concretely, the objective is defined by the dataset, the objective function, and the evaluation metrics, and each benchmark module is consist of these three terms. For example, the benchmark flgo.benchmark.mnist_classification requires a model to perform correct classification on hand written digits images, which is evaluated by the accuracy.
On the other hand, the data distribution suggests how the data is distributed among participants. For example, each participent may owns data that is identically and independently sampled from a global dataset, which is called the i.i.d. case. In our framework, Paritioner is responsible for creating such data distributions.
In our framework, we use the configuration of benchmark and partitioner to generate federated tasks. We now take a example to show how to write configurations to generate different data distributions on the same given benchmark.
1.3.1 Example: MNIST classification under different data distributions
Firstly, each config is of the type dict in python. The key 'benchmark' and 'partitioner' repsectively specify the information about the aforementioned benchmark and Partitioner.
import flgo
flgo.set_data_root('cwd') # change the directory storing raw data to the current working directory
import flgo.benchmark.mnist_classification as mnist
import flgo.algorithm.fedavg as fedavg
import flgo.benchmark.partition
import os
# DiversityPartitioner will allocate the data to clients w.r.t. data diversity (e.g. here is label diversity)
# DirichletPartitioner will allocate the data to clients w.r.t. dirichlet distribution on specific attr. (e.g. here is also label)
config_iid = {'benchmark':mnist,'partitioner':{'name': flgo.benchmark.partition.IIDPartitioner,'para':{'num_clients':100}}}
config_div01 = {'benchmark':mnist,'partitioner':{'name': flgo.benchmark.partition.DiversityPartitioner,'para':{'num_clients':100, 'diversity':0.1}}}
config_div05 = {'benchmark':mnist,'partitioner':{'name': flgo.benchmark.partition.DiversityPartitioner,'para':{'num_clients':100, 'diversity':0.5}}}
config_div09 = {'benchmark':mnist,'partitioner':{'name': flgo.benchmark.partition.DiversityPartitioner,'para':{'num_clients':100, 'diversity':0.9}}}
config_dir01 = {'benchmark':mnist,'partitioner':{'name': flgo.benchmark.partition.DirichletPartitioner,'para':{'num_clients':100, 'alpha':0.1}}}
config_dir10 = {'benchmark':mnist,'partitioner':{'name': flgo.benchmark.partition.DirichletPartitioner,'para':{'num_clients':100, 'alpha':1.0}}}
config_dir50 = {'benchmark':mnist,'partitioner':{'name': flgo.benchmark.partition.DirichletPartitioner,'para':{'num_clients':100, 'alpha':5.0}}}
task_dict = {
'./mnist_iid': config_iid,
'./mnist_div01': config_div01,
'./mnist_div05': config_div05,
'./mnist_div09': config_div09,
'./mnist_dir01': config_dir01,
'./mnist_dir10': config_dir10,
'./mnist_dir50': config_dir50,
}
for task in task_dict:
if not os.path.exists(task):
flgo.gen_task(task_dict[task], task)
Data root directory has successfully been changed to /home/wz/xw_d2l/Jupyter
Secondly, use FedAvg to optimize these tasks with the same hyper-parameters. Note that each benchmark will be attached with a default model (e.g. a predefined CNN for mnist_classification), and initialization without specifying model will automatically load the default model.
import flgo.algorithm.fedavg as fedavg
option = {'gpu':0, 'num_rounds':20, 'num_epochs':1, 'learning_rate':0.1, 'batch_size':64, 'eval_interval':2}
runners = [flgo.init(task, fedavg, option) for task in task_dict]
for runner in runners:
runner.run()
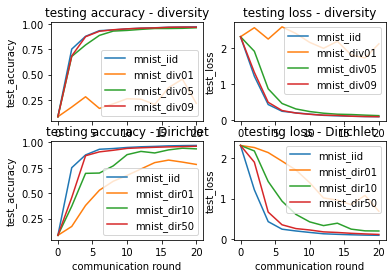
Thirdly, use flgo.experiment.analyzer to read the records and visuazlie the results.
import flgo.experiment.analyzer as al
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
div_recs = al.Selector({'task':[t for t in task_dict if 'iid' in t or 'div' in t], 'header':['fedavg']})
plt.subplot(221)
for task in div_recs.tasks:
rec_list = div_recs.records[task]
for rec in rec_list:
plt.plot(rec.data['communication_round'], rec.data['test_accuracy'], label=task.split('/')[-1])
plt.title('testing accuracy - diversity')
plt.ylabel('test_accuracy')
plt.xlabel('communication round')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(222)
for task in div_recs.tasks:
rec_list = div_recs.records[task]
for rec in rec_list:
plt.plot(rec.data['communication_round'], rec.data['test_loss'], label=task.split('/')[-1])
plt.title('testing loss - diversity')
plt.ylabel('test_loss')
plt.xlabel('communication round')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(223)
dir_recs = al.Selector({'task':[task for task in task_dict if 'iid' in task or 'dir' in task], 'header':['fedavg']})
for task in dir_recs.tasks:
rec_list = dir_recs.records[task]
for rec in rec_list:
plt.plot(rec.data['communication_round'], rec.data['test_accuracy'], label=task.split('/')[-1])
plt.title('testing accuracy - Dirichlet')
plt.ylabel('test_accuracy')
plt.xlabel('communication round')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(224)
dir_recs = al.Selector({'task':[task for task in task_dict if 'iid' in task or 'dir' in task], 'header':['fedavg']})
for task in dir_recs.tasks:
rec_list = dir_recs.records[task]
for rec in rec_list:
plt.plot(rec.data['communication_round'], rec.data['test_loss'], label=task.split('/')[-1])
plt.title('testing loss - Dirichlet')
plt.ylabel('test_loss')
plt.xlabel('communication round')
plt.legend()
plt.show()