Index
Install FLGo
Install FLGo through pip.
pip install flgo
If the package is not found, please use the command below to update pip
pip install --upgrade pip
Create Your First Federated Task
Here we take the classical federated benchmark, Federated MNIST [1], as the example, where the MNIST dataset is splitted into 100 parts identically and independently.
import flgo
import os
# the target path of the task
task_path = './my_first_task'
# create task configuration
task_config = {'benchmark':{'name': 'flgo.benchmark.mnist_classification'}, 'partitioner':{'name':'IIDPartitioner', 'para':{'num_clients':100}}}
# generate the task if the task doesn't exist
if not os.path.exist(task_path):
flgo.gen_task(task_config, task_path)
After running the codes above, a federated dataset is successfully created in the task_path. The visualization of the task is stored in
task_path/res.png as below

Run FedAvg to Train Your Model
Now we are going to run the classical federated optimization algorithm, FedAvg [1], on the task created by us to train a model.
import flgo.algorithm.fedavg as fedavg
# create fedavg runner on the task
runner = flgo.init(task, fedavg, {'gpu':[0,],'log_file':True, 'num_steps':5})
runner.run()
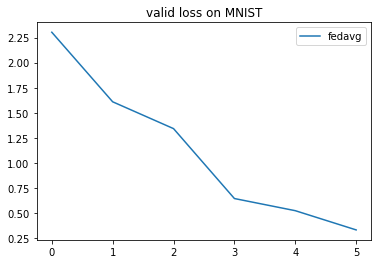
Show Training Result
The training result is saved as a record under the dictionary of the task task_path/record. We use the built-in analyzer to read and show it.
import flgo.experiment.analyzer
# create the analysis plan
analysis_plan = {
'Selector':{'task': task_path, 'header':['fedavg',], },
'Painter':{'Curve':[{'args':{'x':'communication_round', 'y':'val_loss'}}]},
'Table':{'min_value':[{'x':'val_loss'}]},
}
flgo.experiment.analyzer.show(analysis_plan)