2.2.1 Example: FedProx
In this section, we discuss how to realize ideas with modification on the local training phase in FL. We take the method FedProx as the example. FedProx is proposed by Li Tian in 2018 and accepted by MLSys2020. It addresses the data and system heterogeneity problem in FL, which has made two major improvements over FedAvg:
- Sample & Aggregation: sample clients by the probability w.r.t. the ratios of local data sizes (i.e. MD sampling) and uniformly aggregates the received models (i.e. uniform aggregation)
- Local Training: optimize a proxy \(L'\) of original local objective by additionally adding proximal term on it
where \(k\) denoting the \(k\)th client, \(t\) denoting the communication round, and \(i\) denoting the \(i\)th local training iterations. \(\mu\) is the hyper-parameter of FedProx.
2.2.2 Implementation
Since we have already implemented MD sampling and uniform aggregation as preset options, we only consider how to customize the local training process here.
2.2.2.1 Add hyper-parameter
We provide the API Server.init_algo_para(algo_para: dict) for adding additional algorightm-specific hyper-parameters. The definition of the method is as follows:
def init_algo_para(self, algo_para: dict):
"""
Initialize the algorithm-dependent hyper-parameters for the server and all the clients.
Args:
algo_paras (dict): the dict that defines the hyper-parameters (i.e. name, value and type) for the algorithm.
Example:
```python
>>> # s is an instance of Server and s.clients are instances of Client
>>> s.u # will raise error
>>> [c.u for c in s.clients] # will raise errors too
>>> s.init_algo_para({'u': 0.1})
>>> s.u # will be 0.1
>>> [c.u for c in s.clients] # will be [0.1, 0.1,..., 0.1]
```
Note:
Once `option['algo_para']` is not `None`, the value of the pre-defined hyperparameters will be replaced by the list of values in `option['algo_para']`,
which requires the length of `option['algo_para']` is equal to the length of `algo_paras`
"""
...
The key-value pairs in algo_para corresponds to the names of the hyper-parameters and their defalut values. After calling this method, instances of both Server and Client can directly access the hyper-parameter by self.parameter_name. An example is as shown in the definition. This method is usually called in the initialize method of the server. Now we add the hyper-parameter \(\mu\) for FedProx and set its default value as 0.1.
import flgo.algorithm.fedbase as fedbase
import flgo.utils.fmodule as fmodule
class Server(fedbase.BasicServer):
def initialize(self, *args, **kwargs):
# set hyper-parameters
self.init_algo_para({'mu':0.01})
# set sampling option and aggregation option
self.sample_option = 'md'
self.aggregation_option = 'uniform'
2.2.2.2 Modify local objective
import copy
import torch
class Client(fedbase.BasicClient):
@fmodule.with_multi_gpus
def train(self, model):
# record the global parameters
src_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
# freeze gradients on the copy of global parameters
src_model.freeze_grad()
# start local training
model.train()
optimizer = self.calculator.get_optimizer(model, lr=self.learning_rate, weight_decay=self.weight_decay, momentum=self.momentum)
for iter in range(self.num_steps):
# get a batch of data
batch_data = self.get_batch_data()
model.zero_grad()
# compute the loss of the model on batched dataset through task-specified calculator
loss = self.calculator.compute_loss(model, batch_data)['loss']
# compute the proximal term
loss_proximal = 0
for pm, ps in zip(model.parameters(), src_model.parameters()):
loss_proximal += torch.sum(torch.pow(pm - ps, 2))
loss = loss + 0.5 * self.mu * loss_proximal
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
return
2.2.2.3 Create new class fedprox
Implement FedProx as a new class like
class my_fedprox:
Server = Server
Client = Client
2.2.3 Experiment
Now let's take a look on the experimental results on the fedprox. We consider the experimental settings in Sec.1.3.1.
import flgo
import os
# generate federated task
task = './test_synthetic'
config = {'benchmark':{'name':'flgo.benchmark.synthetic_regression', 'para':{'alpha':0.5, 'beta':0.5, 'num_clients':30}}}
if not os.path.exists(task): flgo.gen_task(config, task_path = task)
# running methods
import flgo.algorithm.fedavg as fedavg
option = {'num_rounds':200, 'num_epochs':5, 'batch_size':10, 'learning_rate':0.1, 'gpu':0}
fedavg_runner = flgo.init(task, fedavg, option=option)
my_fedprox_runner = flgo.init(task, my_fedprox, option=option)
fedavg_runner.run()
my_fedprox_runner.run()
# show results
import flgo.experiment.analyzer
analysis_plan = {
'Selector':{
'task': task,
'header':['fedavg', 'my_fedprox_mu0.01'],
'filter':{'R':200}
},
'Painter':{
'Curve':[
{'args':{'x': 'communication_round', 'y':'test_loss'}, 'fig_option':{'title':'test loss on Synthetic'}},
{'args':{'x': 'communication_round', 'y':'test_accuracy'}, 'fig_option':{'title':'test accuracy on Synthetic'}},
]
}
}
flgo.experiment.analyzer.show(analysis_plan)
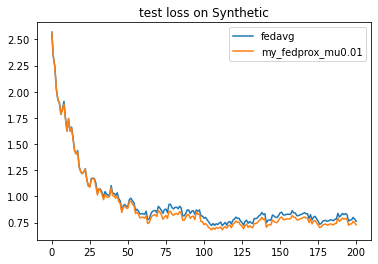
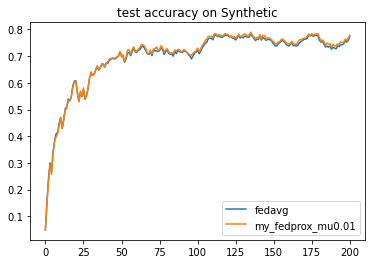
2.2.3.1 Change values of hyper-parameters
We change the value of hyper-parameter \(\mu\) by specifying the keyword algo_para in option
option01 = {'algo_para':0.1, 'num_rounds':200, 'num_epochs':5, 'batch_size':10, 'learning_rate':0.1, 'gpu':0}
option10 = {'algo_para':10.0, 'num_rounds':200, 'num_epochs':5, 'batch_size':10, 'learning_rate':0.1, 'gpu':0}
my_fedprox001_runner = flgo.init(task, my_fedprox, option=option01)
my_fedprox001_runner.run()
my_fedprox100_runner = flgo.init(task, my_fedprox, option=option10)
my_fedprox100_runner.run()
analysis_plan = {
'Selector':{
'task': task,
'header':['fedavg', 'my_fedprox'],
'filter':{'R':200}
},
'Painter':{
'Curve':[
{'args':{'x': 'communication_round', 'y':'test_loss'}, 'fig_option':{'title':'test loss on Synthetic'}},
{'args':{'x': 'communication_round', 'y':'test_accuracy'}, 'fig_option':{'title':'test accuracy on Synthetic'}},
]
}
}
flgo.experiment.analyzer.show(analysis_plan)
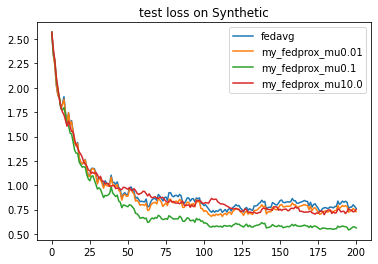
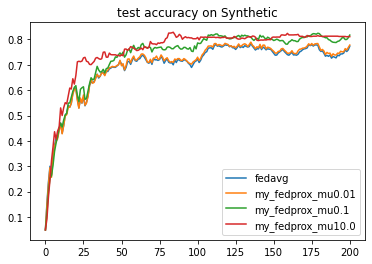
The results suggest that increasing \(\mu\) significantly improves the performance of FedProx on this task.